Introduction to Options Trading
Options trading represents a vital aspect of modern financial markets, providing investors with opportunities to hedge, speculate, or enhance their portfolios. In fact one might say that learning to trade options in today’s financial world “Is not an option”, it is a necessity to take full advantage of all the markets have to offer. Unlike traditional stock trading, where ownership of a security is exchanged, options are financial derivatives that grant traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This distinction is essential, as it allows for a range of strategies and risk management techniques not available in standard stock transactions.
The two fundamental options are known as calls and puts. A call option gives the holder the right to buy an underlying asset, usually at a set price, while a put option provides the right to sell the asset under similar conditions. Understanding the mechanisms of both calls and puts is crucial for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of options trading effectively. These derivatives offer unique strategic flexibility, enabling traders to profit in various market conditions, whether bullish or bearish.
In essence, grasping the intricacies of options trading, particularly calls and puts, forms the foundation upon which successful trading strategies can be built. By delving into options, traders can diversify their approaches, mitigate risks, and enhance their overall investment outcomes in the financial markets.
What are Calls and Puts?
The two primary types of options are calls and puts. These instruments serve distinct purposes in investment strategies, allowing traders to speculate on price movements or hedge existing positions. Understanding their characteristics and functions is essential for anyone looking to engage in options trading.
A call option is a contract that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a specified quantity of an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before a particular expiration date. Calls are positively correlated to the markets direction. This means that the option becomes valuable when the market price of the asset rises above the strike price, allowing the holder to benefit from the increase. Traders typically use calls when they anticipate upward movements in asset prices, enabling them to leverage potential gains while limiting their risk to the premium paid for the option.

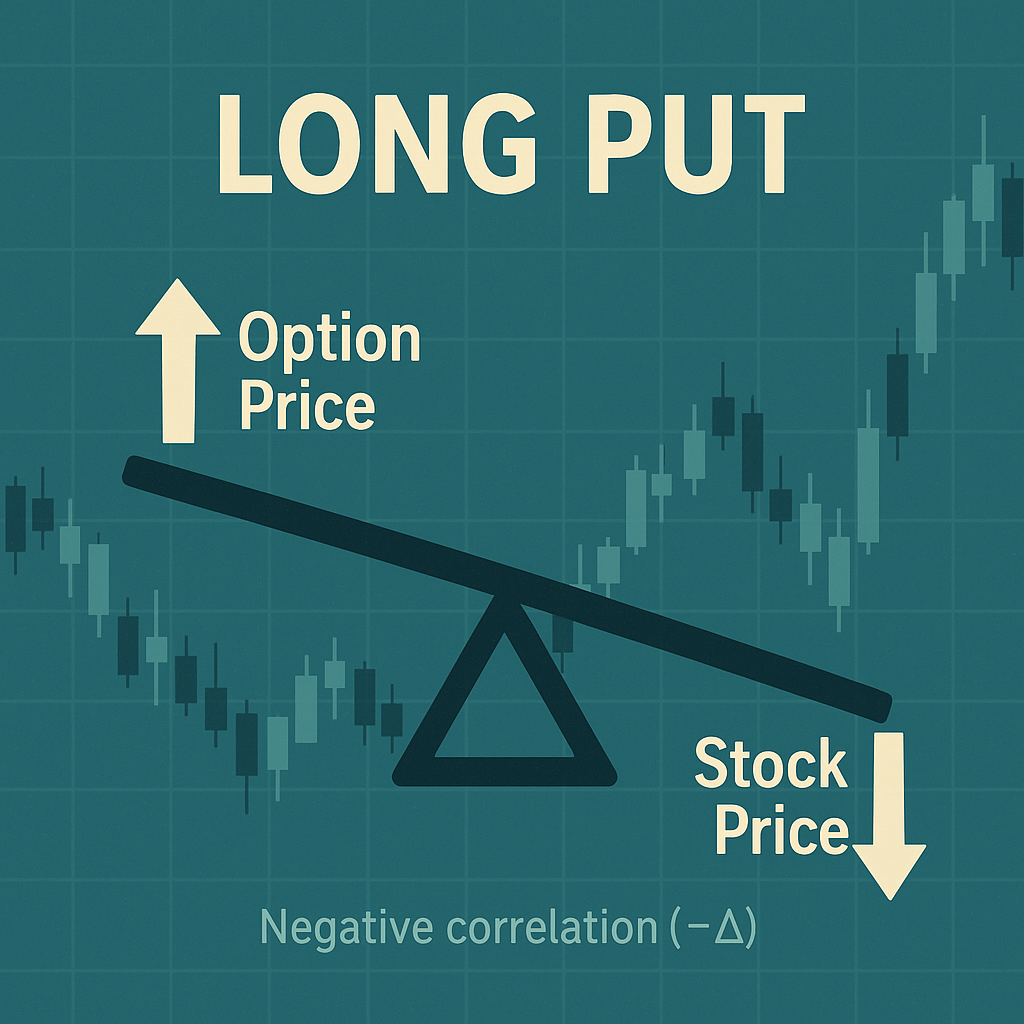
Conversely, a put option provides the buyer with the right to sell an underlying asset at the strike price within a designated timeframe. Put options are negatively correlated to the direction of the underlying. This means that the value of the put option will increase when the market price of the underlying asset declines, as the holder can sell the asset for more than the current market value. Puts are often used not only for speculation but also as a protective measure against falling asset prices, allowing traders to mitigate potential losses in their investment portfolios.
Both calls and puts are fundamental components of options trading and combing them together can offer traders numerous strategies to maximize their potential returns or reduce risks. By mastering the characteristics and functionalities of these contracts, traders can develop informed approaches to their trading activities, positioning themselves efficiently within the marketplace. Ultimately, a solid grasp of calls and puts is essential for anyone aspiring to navigate the complex world of financial instruments effectively.
How Calls and Puts Work in Market Direction
In the realm of options trading, calls and puts serve as vital tools that allow traders to express their market outlook. When traders anticipate a bullish market — that is, they expect the price of an asset to rise — they may decide to purchase call options. This strategy allows them to benefit from potential gains in the underlying asset’s price while limiting their risk to the premium paid for the option. For example, if a trader purchases a call option on a stock currently priced at $100 with a strike price of $110, they can potentially profit if the stock rises above $110 before the option’s expiration date. In this scenario, the profit can be substantial, given that the stock price exceeds the strike price, allowing the trader to purchase the stock at a discount.
On the other hand, when traders expect a bearish market — anticipating that asset prices will decline — they might opt for put options. By purchasing a put option, traders can protect their position or capitalize on the market downturn. For instance, if a trader holds shares of a stock valued at $80 and expects a decline, they can buy a put option with a strike price of $75. If the stock’s price falls below $75, the trader can sell their shares at the higher predetermined price, thus mitigating losses. This method of using options to align with market expectations exemplifies the strategic nature of trading, enabling traders to adjust their positions based on their predictions.
The Importance of Calls and Puts in Options Trading Strategies
When it comes to trading options calls and puts serve as essential building blocks that form the foundation for a number of diverse trading strategies. Understanding calls and puts are crucial for traders who seek to navigate the complexities of the options market effectively.
Calls and puts simplify the decision-making process for traders by offering straightforward mechanisms to express market views. For instance, an investor who believes a stock will rise can purchase call options, thereby securing the right to acquire the stock at a lower price. This leverage can lead to significant profits should the market move favorably. On the other hand, traders suspecting a decline might opt for put options to hedge against potential losses from an existing long position, thereby providing downside protection.
As traders gain proficiency in utilizing calls and puts, they can explore more intricate strategies such as straddles, strangles, and spreads. There are around forty named option strategies that one can trade using a combination of calls and puts. Each of these advanced tactics relies on the foundational knowledge of calls and puts, enabling traders to manage risk and enhance returns through various scenarios. Additionally, the interplay between these two options types encourages strategic thinking, as traders must consider volatility, time decay, and market trends while making their selections. Thus, a solid grasp of calls and puts is invaluable for anyone aspiring to succeed in options trading.
Basic Strategies: Buying and Selling Calls and Puts
The fundamental strategies in options trading revolve around buying and selling calls and puts. Understanding these concepts is critical for any trader seeking to leverage the potential of options to achieve their financial goals. Buying a call option gives the trader the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a specified time frame. This strategy is often employed when one anticipates an increase in the asset’s price. The potential reward is theoretically unlimited, while the maximum loss is capped at the premium paid for the option.
Conversely, buying a put option grants the trader the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price by a specified expiration date. This approach is typically favored when a trader expects a decline in the asset’s price. Similar to calls, the potential for profit can be significant, especially if the asset’s value drops substantially. However, the risk is limited to the premium paid for the put option.
Risk Management in Options Trading
Options trading can present unique opportunities for profit, but it also carries inherent risks that traders must navigate. Understanding the key components of risk management is essential for anyone involved in trading calls and puts. One critical concept to consider is volatility, which refers to the price fluctuations of the underlying asset. High volatility can lead to significant price swings, impacting options premiums. Traders should be aware that while volatility can enhance profit potential, it can also increase the probability of losses, making effective risk management strategies vital.
Another important factor in options trading is time decay, the gradual reduction of an option’s value as it approaches its expiration date. Time decay affects all options, but it particularly impacts out-of-the-money calls and puts. As expiration nears, the rate of time decay accelerates, which can erode profits for long option positions. To mitigate this risk, traders may adopt strategies such as spread trading, which involves buying and selling options simultaneously to offset potential losses while maintaining exposure to favorable price movements.
Strategic thinking is fundamental in minimizing losses in options trading. Setting clear risk parameters, such as stop-loss orders, can help traders limit their exposure to adverse market conditions. Diversification is also a key component in risk management; by spreading investments across different assets, traders can protect their portfolios from the negative impact of unexpected market movements. Additionally, continually educating oneself about market trends and developing adaptable trading strategies can bolster a trader’s ability to navigate volatility and time decay. By prioritizing these risk management techniques, options traders can enhance their chances of achieving consistent success in a complex trading environment.
Market Analysis Techniques for Trading Options
Effective market analysis is pivotal when trading options, as it aids traders in predicting price movements of underlying assets—an essential aspect for successful options strategies. Broadly, market analysis can be categorized into two main techniques: fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Each approach offers unique insights valuable for understanding the market dynamics surrounding calls and puts.
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the value of an asset by examining economic indicators, financial statements, and other qualitative and quantitative factors. Traders employing this method will look at elements such as earnings reports, interest rates, and macroeconomic trends to gauge the overall health of the underlying asset. For instance, a trader might analyze an upcoming earnings report to anticipate whether a stock’s price will rise or fall, thereby informing their options strategies. Such assessments are crucial for investors looking to purchase calls or puts, as they highlight potential price adjustments based on economic news and events.
On the other hand, technical analysis focuses on price patterns, market trends, and various indicators to predict future price movements. This form of analysis does not concern itself with the fundamental aspects of an asset but rather uses historical data, charts, and momentum indicators like the moving average or Relative Strength Index (RSI). Traders often favor technical analysis for its ability to provide concise entry and exit points in a rapidly changing market environment. Particularly for options trading, employing various technical indicators can enhance decision-making and improve the timing of trades involving calls and puts.
Ultimately, the choice between fundamental and technical analysis often depends on the trader’s individual strategy and objectives. Many successful traders find value in combining both methods, as this synchronicity can bolster their understanding of market trends and asset performance, allowing for more informed trading decisions.
The Journey to Advanced Options Strategies
Embarking on the journey to advanced options strategies requires a solid understanding of the foundational elements of options trading, namely calls and puts. Mastery of these basic instruments not only equips traders with essential knowledge but also paves the way for exploring a vast array of more complex strategies. Calls and puts serve as the cornerstone of options trading, offering insights into market movements and enabling traders to speculate on price fluctuations effectively. Understanding the mechanics of these options is crucial; a call option grants the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified price, while a put option allows for selling it. These fundamental concepts are imperative for building more sophisticated trading techniques.
Transitioning from beginner to advanced options strategies necessitates both qualitative and quantitative skill sets. Qualitatively, traders must cultivate analytical skills, enabling them to interpret market trends and gauge the sentiment driving price changes. Recognizing the relationship between various market factors and how they influence the price of calls and puts enhances a trader’s strategic acumen. Quantitatively, traders should develop a sound understanding of risk management principles and the various metrics that drive options pricing, such as implied volatility, delta, and gamma. Familiarity with these trade metrics allows for a more comprehensive analysis of options, laying the groundwork for the strategic application of over 40 advanced strategies.
Examples of these advanced strategies include spreads, straddles, and iron condors, each requiring a nuanced understanding of options and market behavior. As traders become proficient with calls and puts, they can then venture into these intricate strategies with greater confidence and skill. Ultimately, successfully navigating the world of advanced options trading hinges on the ability to build upon foundational knowledge, continually expanding one’s skill set and market understanding while mitigating risk.
Conclusion: The Path to Becoming a Successful Options Trader
Success in options trading hinges upon a solid understanding of its fundamental components, including calls and puts. These two basic types of options form the bedrock of trading strategies, enabling traders to execute various financial maneuvers based on market conditions. Grasping how calls and puts function not only enhances one’s comprehension of the options market but also equips traders with the necessary tools to navigate its complexities confidently.
For new traders, focusing on calls and puts serves as an essential stepping stone. By mastering these concepts, traders can start formulating strategies that align with their risk tolerance and investment objective. Whether one aims to hedge against market volatility or seek profitable opportunities, understanding the basic building blocks of calls and puts allows for the development of a robust trading plan.
Moreover, continuous learning and adapting to market changes are vital in this journey. As the options market evolves, so should the strategies employed by traders. Engaging with resources such as trading courses, webinars, or mentorship can be invaluable. Embracing volatility and practicing patience can also lead to improved trading results. Markets can be unpredictable, but a well-rounded education on options, particularly calls and puts, significantly elevates a trader’s prospects for success.
In summary, the foundation of successful options trading is built on a thorough understanding of calls and puts. By committing to mastering these basics and staying informed about market trends, traders can pave their way towards achieving proficiency and resilience in the challenging world of options trading.



